A. GRADUATE PROFILE
“To become an expert in geographic remote sensing capable of utilizing geographic information systems to enhance their general skills in solving spatial, environmental, and regional issues.”
B. CURRICULUM STRUCTURE
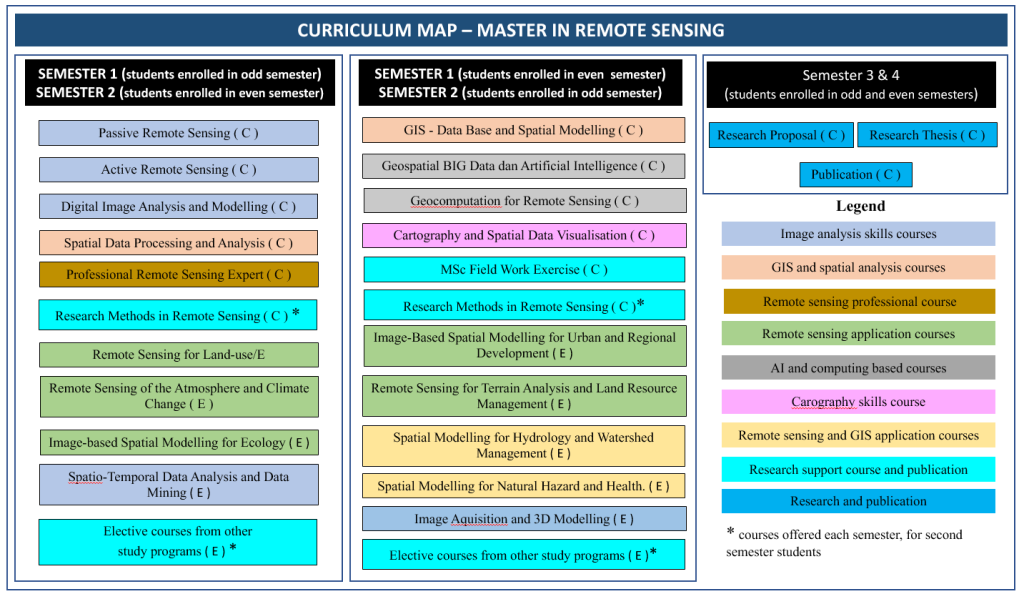
The curriculum of the Master in Remote Sensing at the Faculty of Geography Universitas Gadjah Mada focuses on processing, analysis and spatial modelling of urban, agriculture, forestry, disaster, natural resource management, and other applications using remote sensing data. This programme offers two program streams: regular and by-research programs. Students taking the regular program are required to take a minimum of 44 SKS (98 ECTS) to graduate and 38-40 SKS (108-110 ECTS) for the by-research program. The regular program takes more course credit than the by-research program. In contrast, the by-research program has more research components than the regular program. Tables 6 and 7 show compulsory and elective courses offered at Master in Remote Sensing
Table 1. Compulsory courses and credits at Master in Remote Sensing.
| No | Code | Compulsory Courses | SKS | ECTS* |
| 1 | GEPJ222101 | Passive Remote Sensing | 2 | 4 |
| 2 | GEPJ222102 | Active Remote Sensing | 2 | 4 |
| 3 | GEPJ222103 | Digital Image Analysis and Modelling | 2 | 4 |
| 4 | GEPJ222104 | Spatial Data Processing and Analysis | 3 | 6 |
| 5 | GEPJ222105 | Professional Remote Sensing Expert | 2 | 4 |
| 7 | GEPJ222212 | GIS – Data Base and Spatial Modelling | 3 | 6 |
| 8 | GEPJ222213 | Geospatial Big Data dan Artificial Intelligence | 2 | 4 |
| 9 | GEPJ222214 | Geocomputation for Remote Sensing | 2 | 4 |
| 10 | GEPJ222215 | Cartography and Spatial Data Visualisation | 2 | 4 |
| 11 | GEPJ222106 | Research Methods in Remote Sensing | 2 | 4 |
| 12 | GEPJ222222 | MSc Field Work Exercise | 2 | 4 |
| 13 | GEP6999 | MSc Thesis (proposal + thesis) | 10 | 30 |
| 14 | GEP7002 | MSc Thesis (by-research program) | 15 | 45 |
| 15 | GEP7001 | Thesis Proposal (by-research program) | 3 | 9 |
| 16 | GEP7004 | Research Seminar (by-research program) | 2 | 6 |
| 17 | GEP7003 | Thesis Publication (by-research program) | 12 | 36 |
* 1 SKS of courses equal to 2 ECTS, and 1 SKS of thesis components equal to 3 ECTS.
Table 2. Elective courses and credits at Master in Remote Sensing.
| No | Code | Elective Courses | SKS | ECTS |
| 1 | GEPJ222107 | Remote Sensing for Land-use | 2 | 4 |
| 2 | GEPJ222108 | Remote Sensing of the Ocean and Coastal Area | 2 | 4 |
| 3 | GEPJ222109 | Remote Sensing of the Atmosphere and Climate Change | 2 | 4 |
| 4 | GEPJ222110 | Image-based Spatial Modelling for Ecology | 2 | 4 |
| 5 | GEPJ222111 | Spatio-Temporal Data Analysis and Data Mining | 2 | 4 |
| 6 | GEPJ222216 | Remote Sensing for Terrain Analysis and Land Resource Management | 2 | 4 |
| 7 | GEPJ222217 | Spatial Modelling for Hydrology and Watershed Management | 2 | 4 |
| 8 | GEPJ222218 | Spatial Modelling for Natural Hazard and Health. | 2 | 4 |
| 9 | GEPJ222219 | Image-Based Spatial Modelling for Urban and Regional Development | 3 | 6 |
| 10 | GEPJ222220 | Image Acquisition and 3D Modelling | 2 | 4 |
| 11 | Elective courses from other study programmes | 2 | 4 |
The course structure of the regular and by-research programs in Master in Remote Sensing is presented in Table 8 below:
Table 3. Course structure for the regular and by-research programs at Master in Remote Sensing.
| Regular program | By-research program | ||||
| Component | SKS | ECTS | Component | SKS | ECTS |
| Compulsory Courses | 24 | 48 | Compulsory Courses | 4 (Research Methods in Remote Sensing and MSc Field Work Exercise) | 8 |
| Elective Courses | 10 | 20 | Elective Courses | 2 (Thesis support courses) | 4 |
| Thesis | 10 | 30 | Proposal Thesis | 3 | 9 |
| Research Seminar | 2 | 6 | |||
| Thesis | 15 | 45 | |||
| Thesis Publication | 12 | 36 | |||
| Total | 44 | 98 | Total | 38 | 108 |
C. PROGRAM LEARNING OUTCOME
Tabel 4. Program Learning Outcome
| CP/PLO | Description | Bloom’s Taxonomy |
| CPL- A1 | Knowledge :Having in-depth and specific knowledge of remote sensing. | 3. Application (apply, use, demonstrate) |
| CPL-A2 | General Skills : Able to assess the advantages and limitations of remote sensing methods in solving spatial, environmental and regional problems. | 6. Evaluation (appraise, assess,evaluate) |
| CPL-B1 | Specific Skills : Able to assess the advantages and limitations of remote sensing methods in solving spatial, environmental and regional problems. | 4. Analysis (analyse) |
| CPL-B2 | Specific Skills : Able to assess the advantages and limitations of remote sensing methods in solving spatial, environmental and regional problems. | 4. Analysis (analyse) |
| CPL-C1 | Specific Skills, and Attitudes : Able to manage remote sensing survey activities as an individual or in teamwork. | 5. Synthesis (manage, organise, plan) |
| CPL-C2 | Specific Skills, and Attitudes : A ble to compile research-based and publish scientific articles in the field of remote sensing. | 5. Synthesis (arrange, compose, construct) |
The relationship matrix between PLOs and courses is presented in Table 4 below:
Table 5. Modules contribution to PLOs matrix.
D. DEFICIENCY
The Remote Sensing Master’s study program organizes proficiency activities for new students. Deficiency activities are intended so that each student gets basic knowledge of geography. This is because the Master of Remote Sensing can accept students from various scientific disciplines. Students who are required to make up for deficiencies are students with backgrounds other than Bachelor of Cartography and Remote Sensing. Deficiencies are carried out 1 week before lectures start. The following is a list of Deficiency courses (Table 6).
Tabel 6. Mata Kuliah Defisiensi
| No. | Subject | Course Material |
| 1 | Earth Sciences | Introduction to Geology, Geomorphology, Hydrology, Climatology /Meterology and Soil |
| 2 | Remote Sensing Concept | Introduction to RS: Systems, Interpretation Methods and Applications |
| 3 | Visual Interpretation | The main points of visual interpretation techniques with examples (practical) |
| 4 | Principles of Cartography | Understanding maps, mapping methods, map use, map analysis, map projection |
| 5 | Geographic Information System Concept | GIS developments, data models/formats, analysis methods, software examples, applications |
Figure 1 shows the curriculum map of the Master in Remote Sensing.